An operator is a symbol that tells the compiler to perform specific mathematical or logical functions. C language is rich in built-in operators and provides the following types of operators −
- Arithmetic Operators
- Relational Operators
- Logical Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Misc Operators
Arithmetic Operators
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
main() {
int a = 21;
int b = 10;
int c ;
c = a + b;(ADDITION)
printf("Line 1 - Value of c is %d\n", c );
c = a - b;(SUBTRACTION)
printf("Line 2 - Value of c is %d\n", c );
c = a * b;(MULTIPLICATION)
printf("Line 3 - Value of c is %d\n", c );
c = a / b;(DIVIDE)
printf("Line 4 - Value of c is %d\n", c );
c = a % b;(REMAINDER)
printf("Line 5 - Value of c is %d\n", c );
c = a++; (INCREMENT)
printf("Line 6 - Value of c is %d\n", c );
c = a--; (DECREMENT)
printf("Line 7 - Value of c is %d\n", c );
}
Relational Operators
These operators are used to compare the value of two variables.
Operators With Example/Description
>
x > y (x is greater than y)
<
x < y (x is less than y)
>=
x >= y (x is greater than or equal to y)
<=
x <= y (x is less than or equal to y)
==
x == y (x is equal to y)
!=
x != y (x is not equal to y)
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int m=40,n=20;
if (m == n)(Equal)
{
printf("m and n are equal");
}
else
{
printf("m and n are not equal");
}
}
⇒C Complier to run Above code:https://goo.gl/bzuHcQ
Logical Operators
Operators with Example/Description
&& (logical AND)
(x>5)&&(y<5)
It returns true when both conditions are true
|| (logical OR)
(x>=10)||(y>=10)
It returns true when at-least one of the condition is true
! (logical NOT)
!((x>5)&&(y<5))
It reverses the state of the operand “((x>5) && (y<5))”
If “((x>5) && (y<5))” is true, logical NOT operator makes it false
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int m=40,n=20;
int o=20,p=30;
if (m>n && m !=0)
{
printf("&& Operator : Both conditions are true\n");
}
if (o>p || p!=20)
{
printf("|| Operator : Only one condition is true\n");
}
if (!(m>n && m !=0))
{
printf("! Operator : Both conditions are true\n");
}
else
{
printf("! Operator : Both conditions are true. " \
"But, status is inverted as false\n");
}
}
⇒C Complier to run Above code:https://goo.gl/bzuHcQ
Bitwise Operators
Decimal values are converted into binary values which are the sequence of bits and bit wise operators work on these bits.
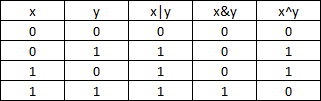
TRUTH TABLE FOR BIT WISE OPERATION & BIT WISE OPERATORS:
Assume A = 60 and B = 13 in binary format, they will be as follows −
A = 0011 1100
B = 0000 1101
-----------------
A&B = 0000 1100
A|B = 0011 1101
A^B = 0011 0001
~A = 1100 0011
Assignment Operators
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| = | Simple assignment operator. Assigns values from right side operands to left side operand | C = A + B will assign the value of A + B to C |
| += | Add AND assignment operator. It adds the right operand to the left operand and assign the result to the left operand. | C += A is equivalent to C = C + A |
| -= | Subtract AND assignment operator. It subtracts the right operand from the left operand and assigns the result to the left operand. | C -= A is equivalent to C = C - A |
| *= | Multiply AND assignment operator. It multiplies the right operand with the left operand and assigns the result to the left operand. | C *= A is equivalent to C = C * A |
| /= | Divide AND assignment operator. It divides the left operand with the right operand and assigns the result to the left operand. | C /= A is equivalent to C = C / A |
| %= | Modulus AND assignment operator. It takes modulus using two operands and assigns the result to the left operand. | C %= A is equivalent to C = C % A |
| <<= | Left shift AND assignment operator. | C <<= 2 is same as C = C << 2 |
| >>= | Right shift AND assignment operator. | C >>= 2 is same as C = C >> 2 |
| &= | Bitwise AND assignment operator. | C &= 2 is same as C = C & 2 |
| ^= | Bitwise exclusive OR and assignment operator. | C ^= 2 is same as C = C ^ 2 |
| |= | Bitwise inclusive OR and assignment operator. | C |= 2 is same as C = C | 2 |
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
main() {
int a = 21;
int c ;
c = a;
printf("Line 1 - = Operator Example, Value of c = %d\n", c );
c += a;
printf("Line 2 - += Operator Example, Value of c = %d\n", c );
c -= a;
printf("Line 3 - -= Operator Example, Value of c = %d\n", c );
c *= a;
printf("Line 4 - *= Operator Example, Value of c = %d\n", c );
c /= a;
printf("Line 5 - /= Operator Example, Value of c = %d\n", c );
c = 200;
c %= a;
printf("Line 6 - %= Operator Example, Value of c = %d\n", c );
c <<= 2;
printf("Line 7 - <<= Operator Example, Value of c = %d\n", c );
c >>= 2;
printf("Line 8 - >>= Operator Example, Value of c = %d\n", c );
c &= 2;
printf("Line 9 - &= Operator Example, Value of c = %d\n", c );
c ^= 2;
printf("Line 10 - ^= Operator Example, Value of c = %d\n", c );
c |= 2;
printf("Line 11 - |= Operator Example, Value of c = %d\n", c );
}
⇒C Complier to run Above code:https://goo.gl/bzuHcQ
Misc Operators ↦ sizeof & ternary
Operators
|
Description
|
&
|
This is used to get the address of the variable.
Example : &a will give address of a.
|
*
|
This is used as pointer to a variable.
Example : * a where, * is pointer to the variable a.
|
Sizeof ()
|
This gives the size of the variable.
Example : size of (char) will give us 1.
|
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int *ptr, q;
q = 50;
/* address of q is assigned to ptr */
ptr = &q;
/* display q's value using ptr variable */
printf("%d", *ptr);
return 0;
}
Great !!
ReplyDeleteNice
ReplyDeleteHi Suraj,
ReplyDeleteI am still struggling to understand the difference between void main(), int main() and main(). Is int main() with return 0 same as void main() ?? Please explain.
Thanks
Bharathkumar AV